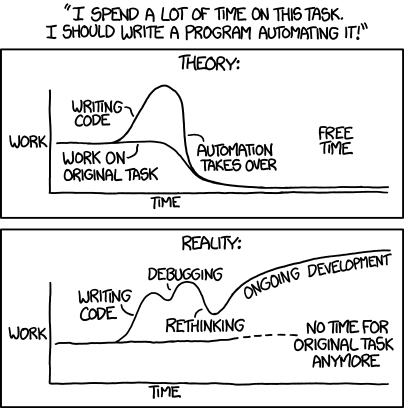
Beginner Lab 2 - Core Shell
Welcome to Lab 2! In this lab you will be learning how to work productively in a shell.
How to submit: create a .txt file (use vim!) with one answer per line for a total of 7 lines. Upload this and your screenshot (see lab for details) to Gradescope.
Don’t forget to use Google and man when stuck. The resources linked at the bottom may be helpful as well.
Setting up
This lab requires a bash shell, vim, and tmux.
If you do not have tmux: apt-get tmux
SSH (Secure Shell)
SSH allows you to log in to a remote computer through the internet.
It is the equivalent of opening a shell on a remote computer.
The usage is ssh [remote username]@[remote host].
Question
- Log on to
tsunami.ocf.berkeley.edu with your OCF username and password. There is a file in ~staff/public_html/decal. Open it. What is the secret in the file?
Pipes and Redirection
Chaining together commands is essential to automating your way through the shell. Here’s a quick cheat sheet:
> : Redirect stdout to a file (Will overwrite the file).
>> : Append stdout to a file (same as > except does not overwrite).
< : Read input from a file.
| : Send output from one program to the input of the next.
Questions
- What line could you use to save the first 10 lines of a file that do not contain any vowels to a new file called
return.txt?
- How could you write
cat output.txt | grep "Cal" without using a pipe?
Other useful tricks
!! can be used to repeat the previous command in the shell.
E.g.
python program.py
sudo !! == sudo python program.py
!:[num] is treated as the previous command’s [num] argument.
E.g.
touch doc.txt
vim !:1 == vim doc.txt
Note: This behavior is from bash and some other shells that implement it.
A quick intro to vim
Why vim?
- It’s a descendant of vi, which was written in Berkeley by Bill Joy, who went on to found Sun Microsystems.
- Sometimes you will be suddenly thrown into
vim via merging git conflicts or other programs.
- It’s included in practically every UNIX environment.
- You can be very productive when familiar with it.
Hello World
Vim is a modal text editor, meaning that you can change editing modes in order to do different things. There are 3 primarily used modes: **Normal**, **Insert**, and **Visual** mode. #### Normal mode: - Used for moving around and editing text - `hjkl` to move left, up, down, and right - `G` to move to end of file, `gg` to move to beginning - `i` to enter **i**nsert mode (`a`, `o` also change mode in different ways) - `dd` to cut a line - `yy` to copy a line - `p` to paste - `/` to search - `u` to undo - Type in commands with `:` - Save with `:w` - Exit with `:q` - Explore more commands online!
Insert mode:
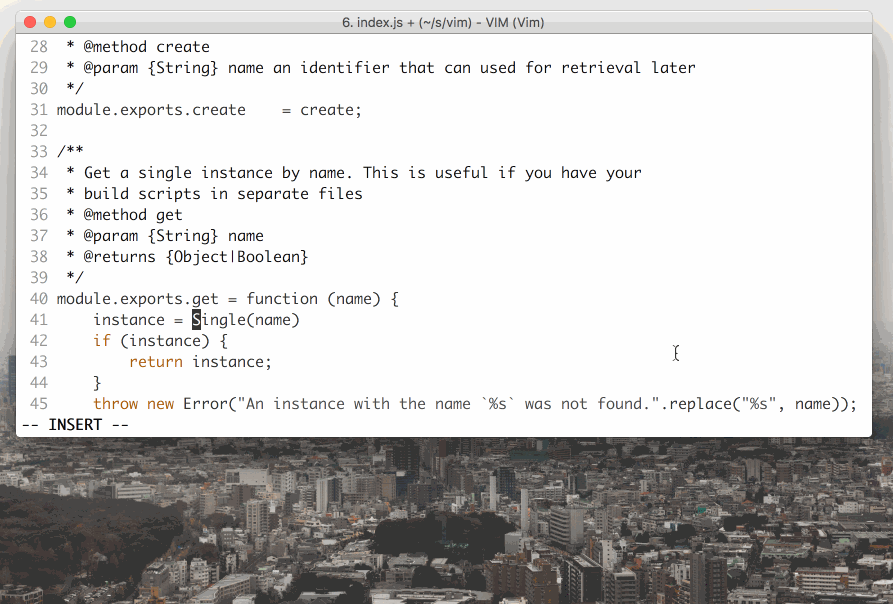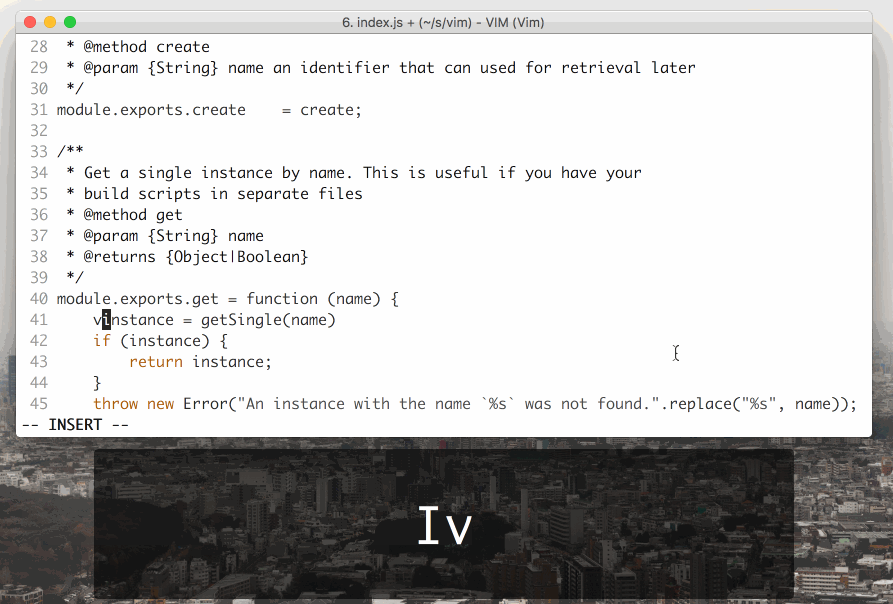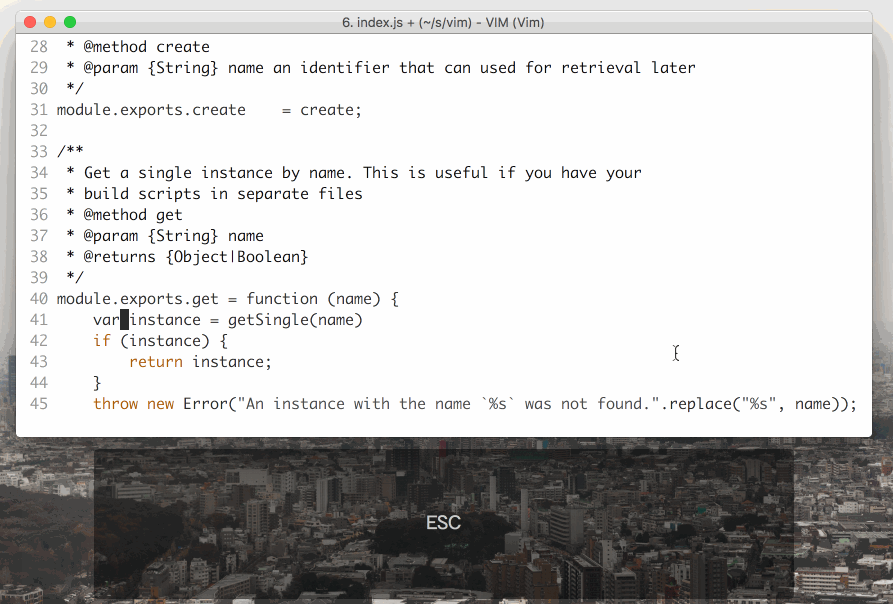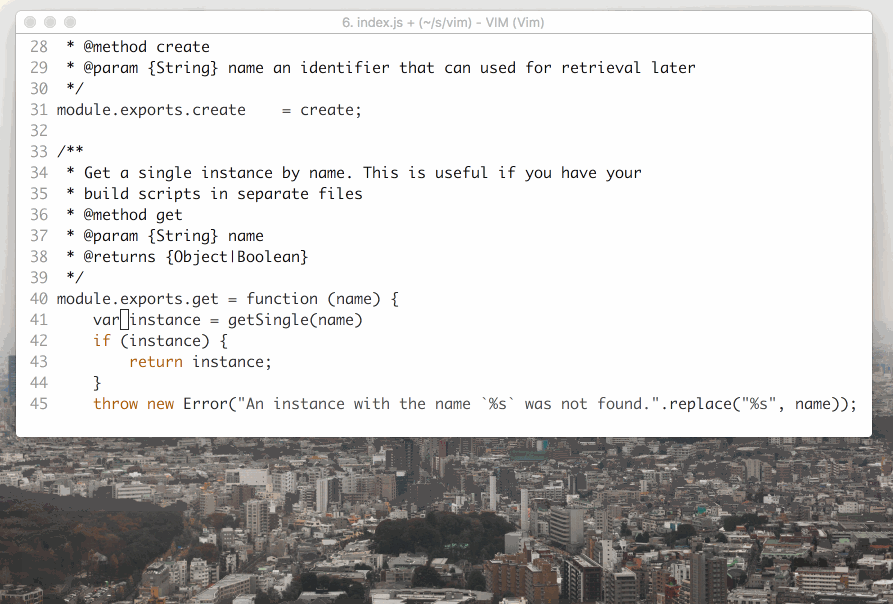
- Used for editing text like a usual editor
- Arrow keys to move
- Esc to exit to normal mode (lots of people bind it to Caps Lock)
Visual mode:
- Enter with
v from normal mode
- Used to select text visually
- Modify selection with normal mode movement commands
- Use
o to move the cursor to the other side of the selection
- Yanking, deleting, and pasting use
y, d, p (sound familiar?)
A key feature of vim is chaining together commands.
Normal mode is essentially a massive amount of shortcuts that you can combine to quickly navigate and edit a file.
Want to move down 3 lines?
You know that j means move down 1 line, so you can use 3j to move down 3.
d is for deletion and w is to jump to the next word, so what does dw do?
Questions
Try playing around with lab2.md while looking up some new commands. Use wget to download it!
- How would you delete the previous 10 lines?
- How would you jump back to the shell without exiting
vim?
- How would you edit a new file alongside another file?
- How would you indent a block of text?
If you’re interested in emacs instead
A quick intro to tmux
Why tmux?
- You can open multiple windows when sshed into a machine.
- You can go compile and run programs while editing them.
- You can logout and ssh back in without having to reopen all your files.
Getting Started:
- Start a session with
tmux.
- Detach from a session with
Ctrl-b d (press d after releasing Ctrl-b)
- Split into 2 panes with
Ctrl-b % (vertical) and Ctrl-b " (horizontal)
- Swap current pane with
Ctrl-b o
Question
- Take a screenshot of a tmux session with multiple windows, panes, and a named window with your username.
Advanced usage (optional)
- Tmux can be used to share your session with others.
- Try remapping shortcuts like the prefix
Ctrl-b to something more convenient.
Ctrl-b [ can be used to scroll around buffers and copy things.
Submitting the lab
Once you’re done remember to submit your text file and screenshot to Gradescope.
There are multiple valid answers for some of the questions.
Don’t be stressed about getting something exactly correct.
Resources
Keybindings
Learning vim progressively
Tmux cheat sheet